- WHAT IS NIPT +
- Indications +
- Test Options +
- Pricing +
- Why Triscreen +
- Technology +
- Methodology +
- Downloads +
- References +
NIPT analyses cell-free DNA from a maternal blood sample (mixture of placental and maternal DNA) to screen for common chromosomal conditions including trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome), and trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome).
Genomewide NIPT screening allows not only for the detection of common chromosomal aneuploidies but provides a comprehensive view of all 23 chromosome pairs. It enables the identification of rare autosomal aneuploidies (RAAs), sex chromosome aneuploidies (SCAs) as well as partial deletions and duplications (also referred to as copy number variations CNVs) that are ≥7 Mb in size.
These additional chromosomal abnormalities have been associated with clinically relevant outcomes such as developmental delays, intellectual disabilities, structural anomalies and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Having insight into these chromosomal abnormalities earlier may assist you and your patient in the management of the pregnancy.
The American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (ACOG) and International Society of Prenatal Diagnosis (ISPD), along with other professional societies, have stated that NIPT is an available screening option for all pregnant women1,8.
NIPT vs. traditional serum screening methods:
- Offers the highest reported detection rate for Down syndrome2
- Offers the lowest reported false positive rate for Down syndrome3
- Offers the broadest screening window (performed as early as 10 weeks gestation until term)2
Next Biosciences is proud to be a valued member of The Global NIPT consortium alongside other Illumina-powered laboratories.
All pregnant women can be offered the option of NIPT.
Patients can be at high risk for aneuploidy due to:
- Maternal age-related risks
- Positive results on maternal-serum screening
- Abnormal ultrasound finding(s)
- History suggestive of increased risk for T21, T18, T13 or sex chromosome aneuploidy
- Parental translocation involving one of the tested chromosomes (depending on size)
Indications for all chromosome test:
- History of a pregnancy with chromosomal abnormality
- Abnormal ultrasound findings and patient wants to avoid invasive test
- One of the parents are known to be a carrier of a balanced translocation (depending on size)
- Patients who want more detailed information and have had a genetic counselling appointment to understand the limitations of the test, and the possibility of false positives and negatives.
Anyone considering genomewide testing is strongly advised to have an appointment with a genetic counsellor / detailed discussion with their obstetrician (regardless of the indication).
-
TriScreen NIPT (Standard Panel)
T21 (Down syndrome), T18 (Edward syndrome), T13 (Patau syndrome)
-
TriScreen NIPT + (All Chromosomes)
Provides chromosomal status for all chromosomes and segmental deletions and duplications >7Mb.
-
Optionally reported
Information on the status of fetal sex chromosomes and certain sex chromosome aneuploidies.
-
Addition of Microdeletions
Chromosome 21, 18, 13 X&Y with 22q deletion only (Di George), 15q11 deletion (Angelman/Prader-Willi), 1p36 deletion, 4p (Wolf-Hirschhorn) 5p (Cri-du-chat)
*Additional blood draw arrangements and logistics are required.
*Please note that Microdeletion samples are currently sent to the United States. -
Rhesus testing
Chromosome 21, 18, 13 X&Y with the addition of fetal RhD status assessment
*Additional blood draw arrangements and logistics are required.
TriScreen NIPT can be performed on:
- Singleton pregnancies
- Twin pregnancies
- Donor pregnancies
- IVF pregnancies (from 8 weeks post-implantation)
- Surrogate pregnancies
|
Screening of cell-free fetal DNA for common chromosomal conditions, |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Chromosome 21 (T21) |
R |
4 100 |
|
Chromosome 21, 18, 13, X&Y |
R |
5 950 |
|
All Chromosomes |
R |
6 500 |
|
Chromosome 21, 18, 13, X&Y & Microdeletions* |
R |
8 500 |
|
All Chromosome & Microdeletions* |
R |
10 500 |
|
|
||
|
Chromosome 21, 18, 13 X&Y, and Fetal RhD |
R |
6 500 |
|
Chromosome 21, 18, 13 X&Y, and 22q11 deletion (Di George) |
R |
6 500 |
*Please note that all prices include VAT and are subject to change.
Powered by Illumina, global leader in next generation sequencing.

Next Biosciences has been offering the Illumina NIPT test in South Africa since 2016.

In-house processing ensuring a quicker turnaround time.
VeriSeqTM NIPT Solution V2, providing the most comprehensive view of genomewide fetal chromosomal anomalies.

1.2% Failure rate (resulting in less re-draws than other tests).
A high accuracy with low fetal fraction - No fetal fraction cut-off (relies on a dynamic threshold (iFact), which reduces NIPT failures).
Access to specialist team of Genetic Scientists, a Medical Doctor, Pathologist and Genetic Counsellor.
One free genetic counselling session for all high risk results, providing your patients with the support they need.

Dedicated client service team to support both you and your patients.

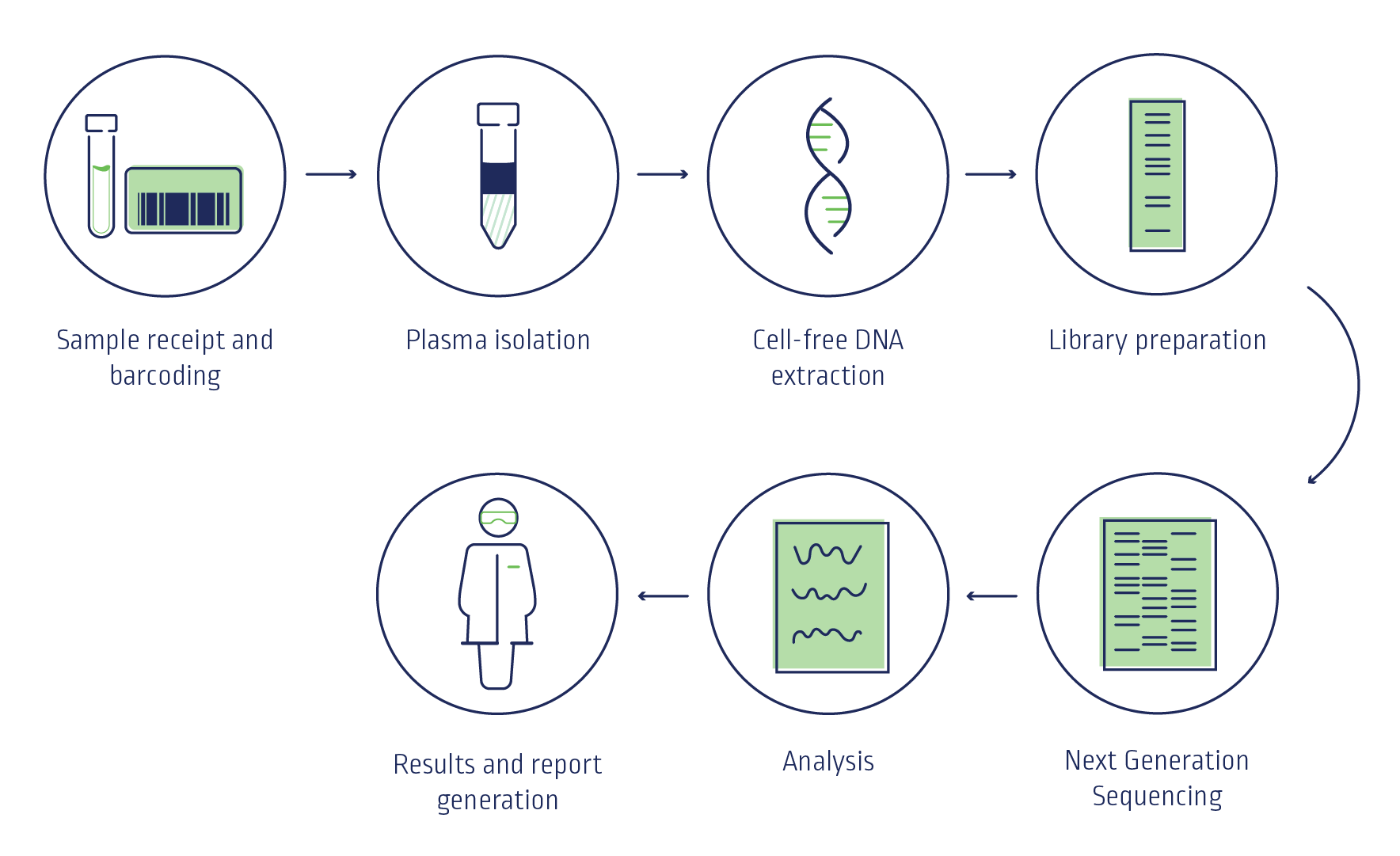
TriScreen NIPT uses whole genome sequencing with next generation sequencing (NGS) technology to analyse cell-free DNA (cfDNA) fragments across the whole genome, which has proven advantages over other NIPT methodologies such as targeted sequencing and array-based methods.
Test failure rates are substantially lower with whole genome sequencing versus other methodologies4, 7-9.
With its high levels of sensitivity and accuracy, NGS produces the data quality needed for reliable analysis of the trace amounts of cfDNA found circulating within blood plasma.
| Benefits of NIPT | Limitations of NIPT |
| Non-invasive with no risk of miscarriage | NIPT is a screening test, not a diagnostic test and must be followed up with an invasive test if a definitive diagnosis is needed. |
| High detection rates for chromosomes tested | In rare instances, results may represent a maternal or placental condition, rather than a fetal condition. |
| High sensitivity and specificity compared to traditional serum screening. |
| Chromosome | N | Sensitivity | 95% CI | Specificity | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trisomy 21 | 2236 | 99.9% (130/130) | 97.1 - 100.0 | 99.90% (1982/1984) | 99.63 - 99.97 |
| Trisomy 18 | 2236 | 99.9% (41/41) | 97.4 - 100.0 | 99.9% (1995/1997) | 99.64 - 99.97 |
| Trisomy 13 | 2235 | 99.9% (14/16) | 87.1 - 100.0 | 99.9% (2000/2002) | 99.64 - 99.97 |
| RAA** | 2300 | 96.4% (27/28) | 82.3 - 99.4 | 99.8% (2001/2005) | 99.49 - 99.92 |
| CNV > 7Mb | 2300 | 74.1% (20/27) | 55.3 - 86.8 | 99.8% (200/2004) | 99.49 - 99.92 |
| Any anomaly*** | 2300 | 95.5% (318/333) | 92.7 - 973 | 99.35% (1954/1967) | 98.87 - 99.61 |
|
*Data from VeriSeq NIPT Solutions v2 package insert
**RAA excludes chromosomes 31, 18, 13 ***Includes sex chromosome anomalies from genomewide screen Key:
N: Sample Size
RAA: Rare Autosomal Aneuploidy
CI: Confidence interval
CNV: Copy number variation
|
|||||
Disclaimer:
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) based on cell-free DNA analysis from maternal blood is a screening test; it is not diagnostic. Test results must not be used as the sole basis for diagnosis. Further confirmatory testing is necessary prior to making any irreversible pregnancy decision.
- Benn P, Borrell A, Chiu R, et al. Position statement from the Chromosome Abnormality Screening Committee on behalf of the board of the International Society for Prenatal Diagnosis. Prenat Diagn. 2015;35(8):725-734.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: Screening for fetal aneuploidy. Obstet Gynecol. 2016;127(5):e123-137.
- Bianchi DW, Parker RL, Wentworth J, et al. DNA sequencing versus standard prenatal aneuploidy screening. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(9):799-808.
- Data calculation on file. Illumina, Inc. 2017.
- VeriSeq NIPT Solution Package Insert.
- Data calculation on file. Illumina, Inc. 2018.
- VeriSeq NIPT Solution v2 Package Insert.
- Committee Opinion No. 640: Cell-free DNA Screening for Fetal Aneuploidy. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126(3):e31-37.
Next Biosciences
Ariane Avenue
International Business Gateway
Cnr. New Road and 6th Road
Midrand, South Africa
Office Hours
Monday - Thursday: 08h00 - 17h00
Friday: 08h00 - 16h00
