- What is stem cell banking +
- Collection process +
- Technology +
- Methodology +
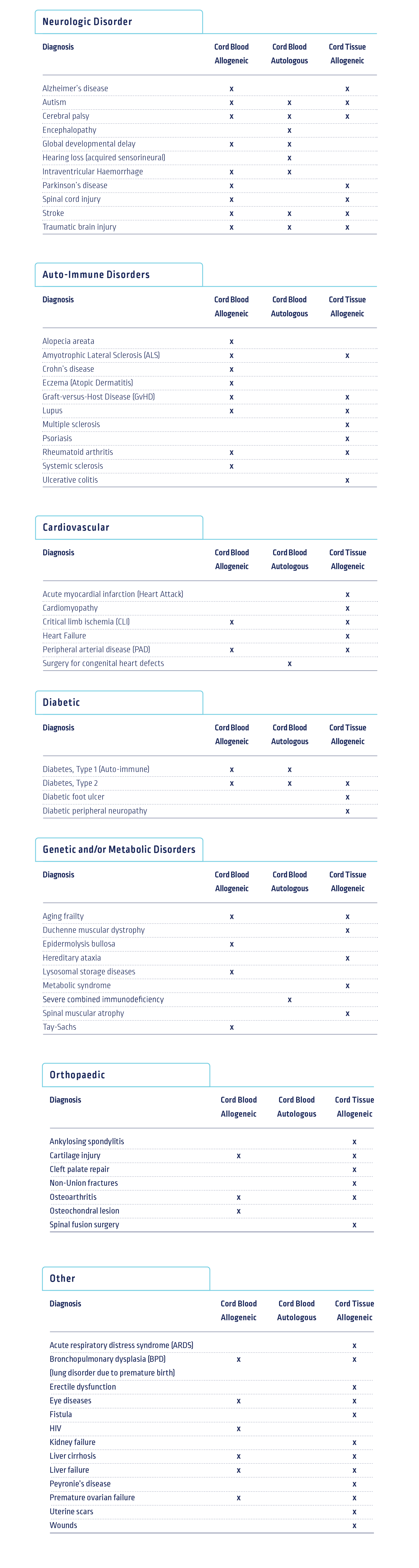
- Standard Therapies +
- Clinical Trials +
- Downloads +
- REFERENCES +
Umbilical stem cell banking harvests the stem cells from the umbilical cord blood and tissue at the birth of a baby.
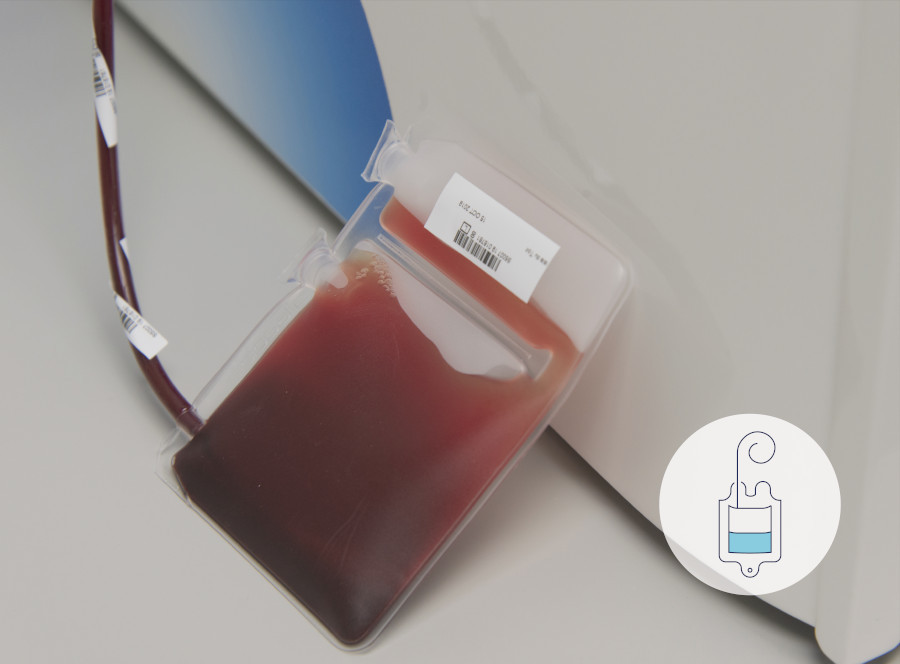

The umbilical cord blood is rich in Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) which can be used to help treat over 80 blood-related diseases.
These stem cells are used in the regeneration of bone marrow and an alternative source of stem cells for a bone marrow transplant.
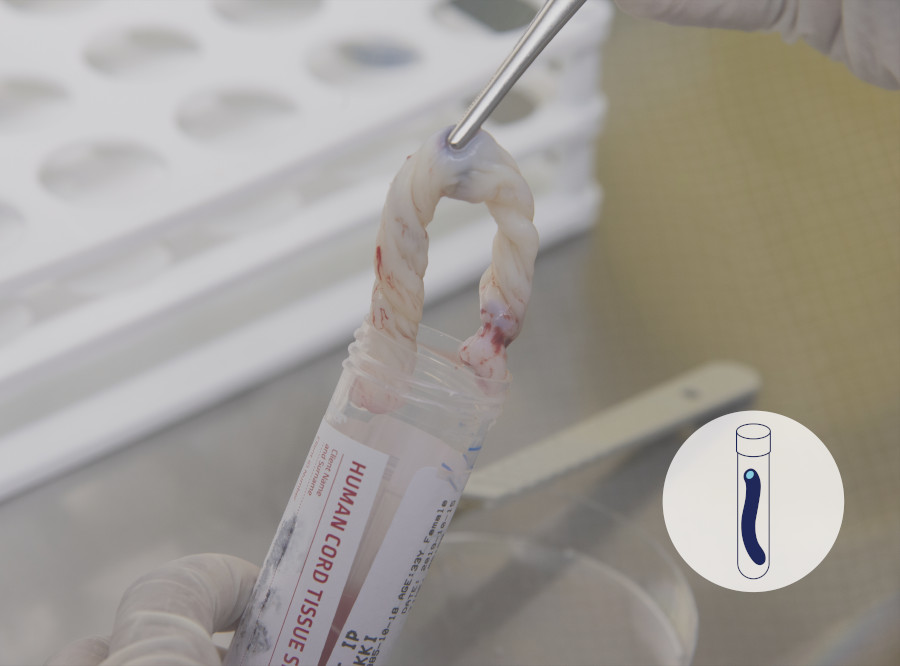
The umbilical cord tissue is rich in Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) which form the connective tissues in our bodies.
These stem cells hold considerable potential in treating a wide variety of medical and aesthetic conditions, such as treating burns or wounds that are battling to heal. They are currently being used in a number of clinical trials.
The collection kit will be brought to the hospital by the patient and the doctor informed of their decision to bank their baby's stem cells.
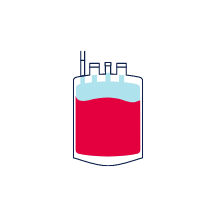
The cord blood is collected immediately after the birth and before delivery of the placenta.
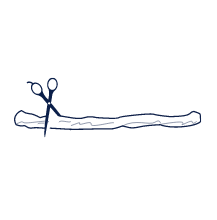
The umbilical cord is cut and clamped.
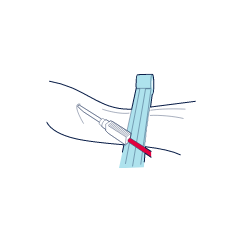
A needle is inserted into the umbilical cord vein and the blood is collected into a sterile bag. The cord can be gently milked to speed up the collection process.
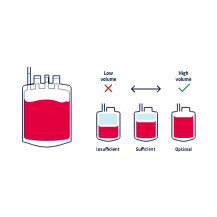
100 - 150ml of cord blood needs to be collected for it to be successfully stored.
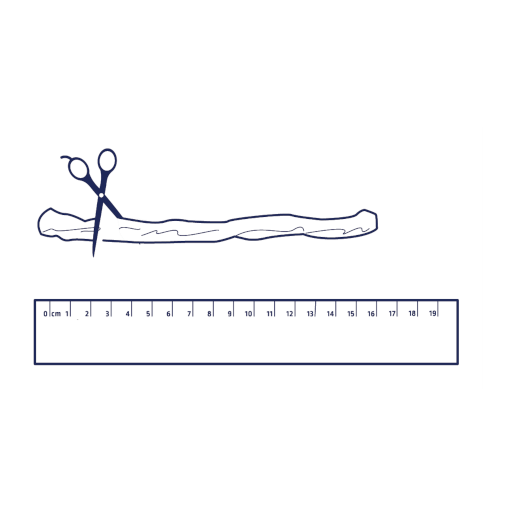
Following the collection of the cord blood, and delivery of the placenta, if the patient has opted for cord tissue storage a 10 - 15cm piece of cord is cut, cleaned and placed inside the sterile collection tube.
If you are unfamiliar with the process, please see our optimal collection video which takes you through a collection.
There are also optimal collection protocols available for download should you prefer.
Netcells makes use of PrepaCyte-CB (Cord Blood)® processing technology when processing the cord blood stem cells.
It was developed in 2009 in the US, specifically for the processing of cord blood. It is a sterile, US FDA 510k approved closed processing system. Netcells chose to adopt this processing method because it recovers more colony forming stem cells, has lower levels of red blood cells post processing and stem cells processed with this method offer a quicker time to engraftment, than other cord blood processing methods1.
PrepaCyte-CB® leads to better separation of the red blood cells from the plasma and white blood cells by a process called sedimentation.
It creates a clear physical difference in separation of cell types, which means it is able to capture more stem cells whilst reducing red blood cells by up to 99%.
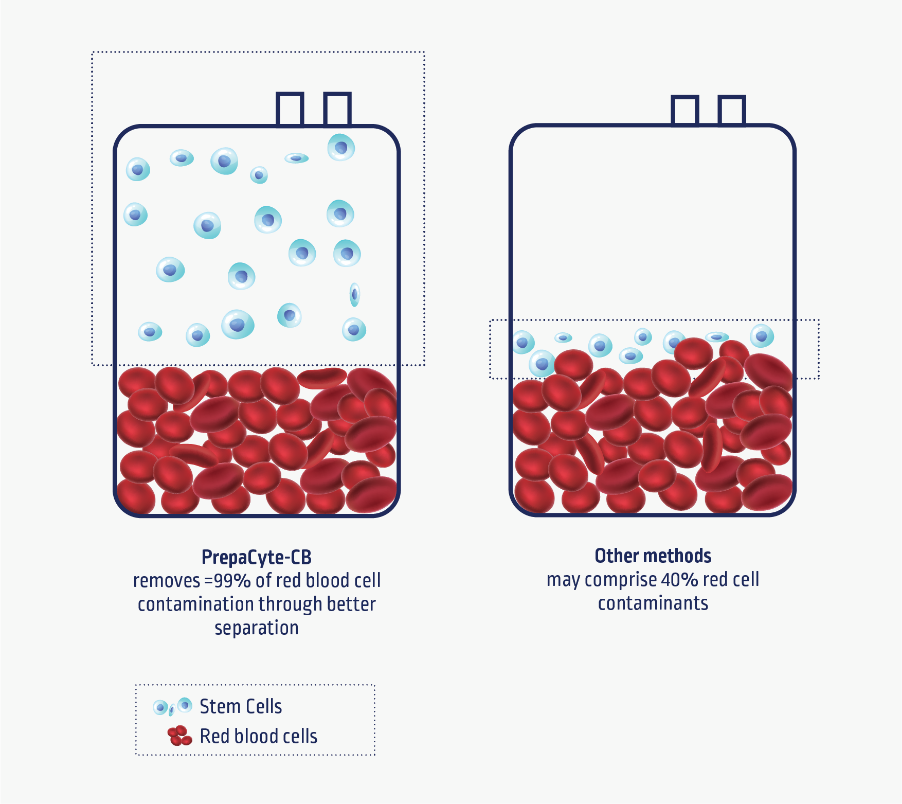
Source: Parent’s Guide to Cord Blood
Next Biosciences
Ariane Avenue
International Business Gateway
Cnr. New Road and 6th Road
Midrand, South Africa
Office Hours
Monday - Thursday: 08h00 - 17h00
Friday: 08h00 - 16h00